The Sun Facts
Sun ['sən]
A huge ball of gas, the star in the center of our solar system
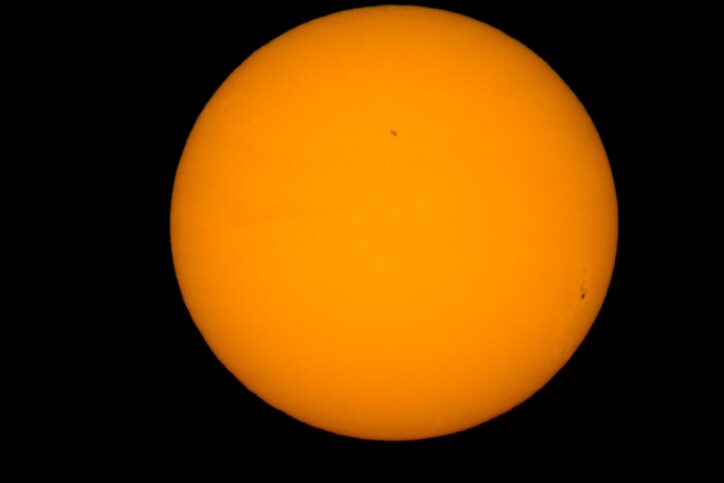

What would happen if there was no Sun? Nothing! The Sun is the source of heat, light, and life on Earth. If there was no sun, our Earth would be dark, cold, and dead. The Sun is even responsible for climate, weather, day and night, and changing seasons on Earth. We have a lot to thank the Sun for!
Long ago, ancient people knew that the Sun was important. Some even thought that the Sun was a god to be worshipped. They believed that the Earth was the center of the universe and that the Sun traveled across the sky every day. In the 1600s, a scientist named Copernicus first proposed that the Sun was the center of our system, and a scientist named Galileo used a special tool called a telescope to observe the sky and prove that the Earth and the other planets revolve around the Sun.
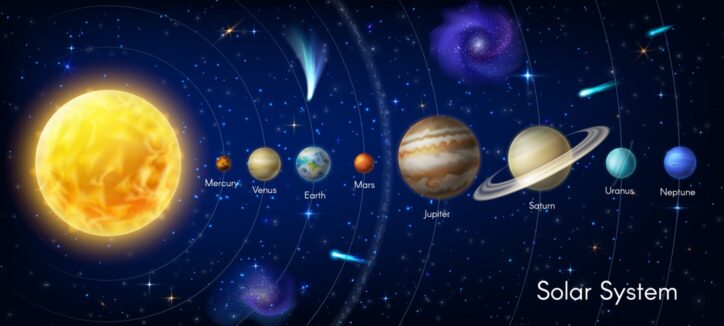
Today we know that the sun is a star, a giant, hot ball of spinning, glowing gases. It is the center of our solar system. Earth and seven other planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) revolve around the Sun in their own unique orbit. Asteroids, dwarf planets, and comets also travel in paths around the Sun. To learn more about the solar system and astronomy, visit these Science Trek sites on Planets and Astronomy.
The Sun: Our Nearest Star
Our Sun is a medium-sized, middle-aged, yellow dwarf star in the Milky Way galaxy, one of billions of stars in the universe. There are many other stars that are larger and brighter than our Sun, but because the Sun is so much closer to us than any of the others, it appears much brighter. And because the Sun is so important to life on Earth, it is very special to us!

How big is the Sun?
The Sun contains 99% of the mass in our solar system, and it is 865,000 miles (1,392,000 kilometers) wide — about 110 times wider than the Earth's diameter. It is huge! About one million Earths could fit inside the Sun. If the Sun were the size of a typical front door, the Earth would be the size of a nickel.
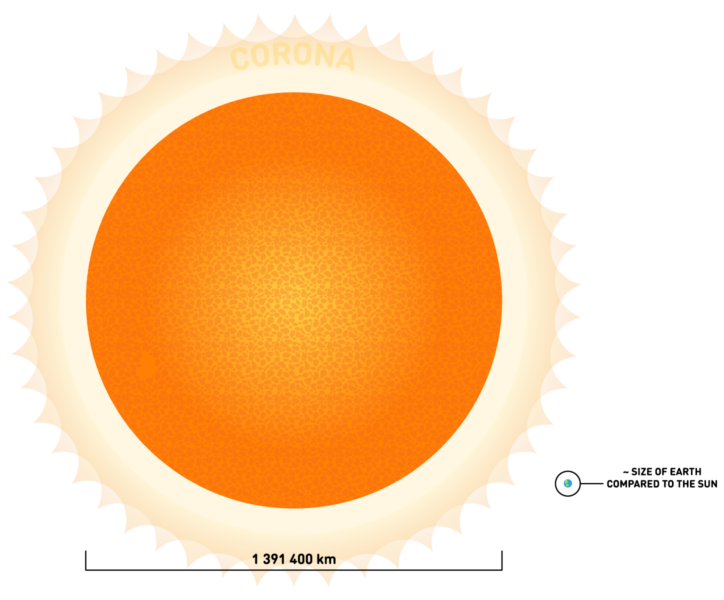
How hot is the Sun?
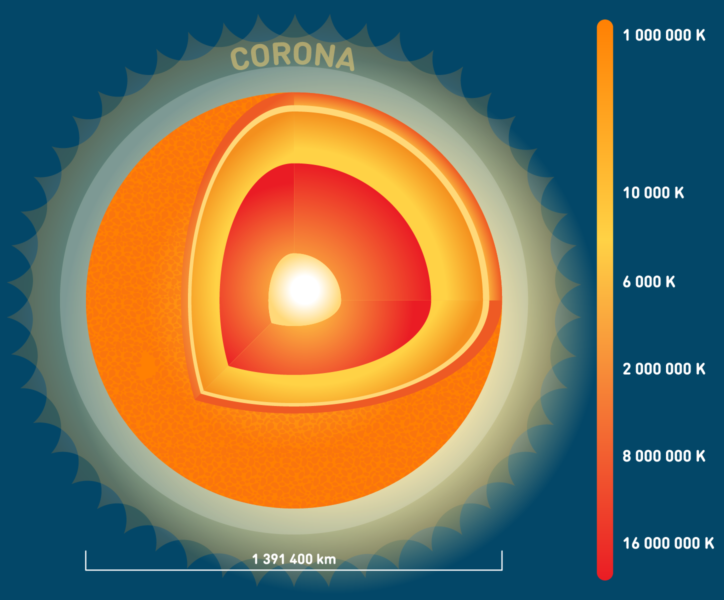
The Sun's surface temperature is around 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit (5500 degrees Celsius), and its core temperature is 29,000,000 degrees Fahrenheit (13,600,00 degrees Celsius). To compare, the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth is 134 degrees Fahrenheit. If a drop-sized piece of the Sun that came from its core was placed on the surface of the Earth, nothing at all would survive for a distance of 93 miles in all directions, from just that one little drop! Although the surface of the Sun is much cooler than the blazing core, it's still hot enough to make carbon rocks (such as diamonds) melt and boil!
How old is the Sun?
The Sun was born about 4.6 million years ago. It formed from a vast, rotating cloud of gas and dust called a solar nebula. Under the force of its own gravity, the gas and dust compressed, spinning faster and faster and flattening into a giant disk. Most of the material was pulled into the center, forming a gas sphere that generated a tremendous amount of heat and pressure. Eventually, its core became hot enough to fuse atoms. At this point, it ignited and became a star — our Sun, producing its own light, heat, and energy. The planets and other components of our solar system formed from the remainder of the disk.

What makes up the Sun?
The Sun is primarily made up of two superheated gases, hydrogen (74%) and helium (24%), with small amounts of other elements. At the center of the Sun, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium atoms, and energy is produced every time the reaction occurs. This process is called nuclear fusion and it is the source of the Sun's power.
Fusion in the core of the Sun generates huge amounts of energy. Every second, 600 million tons of hydrogen are converted into energy! This energy radiates from the core up to the surface of the Sun and then into space. Every hour, the Sun ejects a billion tons of gas into space. The Sun's radiation is in the form of heat, visible light, and other types of energy such as X-rays and ultraviolet light. A portion of the Sun's energy becomes the sunlight that warms and lightens our Earth, providing the means for life.
Like all stars, the Sun has a life cycle. Scientists believe that the Sun is now about halfway through its lifetime, at the stage they call a Yellow Dwarf star. It has used up about half of its supply of hydrogen fuel. However, it has enough to keep going for another 5 billion years, so there is no need to worry! When it runs out of energy, it will go through the stages of becoming a Red Giant and then a White Dwarf star. To learn more, take a tour through the life cycle of stars like our Sun.
The Structure of the Sun
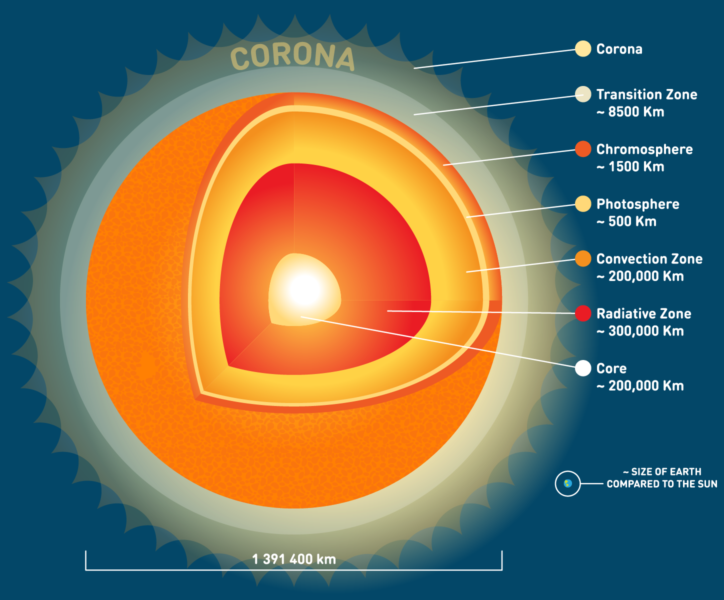
Because our Sun is made of gas, it does not have a solid surface like the Earth. However, the Sun can be divided into several layers of gases: the inner core, the radiation zone, the convection zone, and the photosphere. After the Sun's energy is generated in its core, it passes through the radiation zone. Here the energy moves about randomly; it may take several hundred thousand years for radiation to make its way from the core to the top of the radiation zone. It rises and falls in the convection zone until it passes into the photosphere, which is the visible surface of the Sun that can be viewed with special solar telescopes. This is the layer that releases most of the light that reaches Earth. There are two more layers of gas beyond the photosphere: the chromosphere and the corona. The corona of the Sun is a very hot layer that can only be seen during a solar eclipse. NASA has information and photographs to help you learn more about the structure of the Sun.
The Sun and the Earth
The Sun is about 93 million miles away from Earth, but its effect on the Earth is huge. In the first place, the sun's gravitational pull is what keeps the Earth in orbit around the Sun instead of flying off into space. It takes one full year for the Earth to complete its orbit around the Sun.
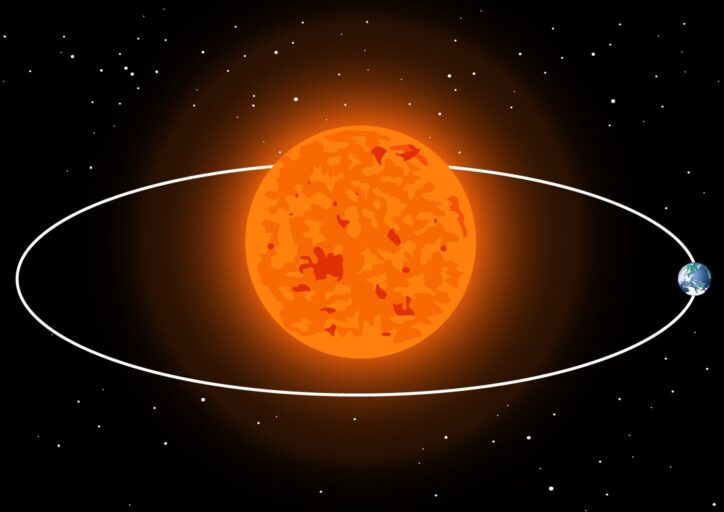
The Sun is the reason for life on this planet. Radiation from the photosphere reaches Earth as sunlight about eight minutes after it leaves the Sun. Not only does the Sun give us direct heat and light so that we can see and stay warm, but it supplies the energy we use every day. Plants, which are the basis of all food chains for animal species, use photosynthesis to harness the sun's energy. Without the sun, we would have nothing to eat!
The energy we get from fossil fuels, such as oil, originally came from the Sun, and solar cells can even convert energy from the Sun directly into electricity.

One of the most obvious effects of the Sun on the Earth is daytime and nighttime. From Earth, the Sun looks like it rises in the morning, moves across the sky in the daytime, and then disappears at night. But it is actually the Earth that is moving. While traveling in its orbit around the Sun, the Earth is also spinning on its axis. One side of the Earth is facing the sun, receiving light and heat — Day. The other side is facing away from the sun into space, where it is dark and cooler — Night. The Earth continues to rotate on its axis, making a full turn every 24 hours.
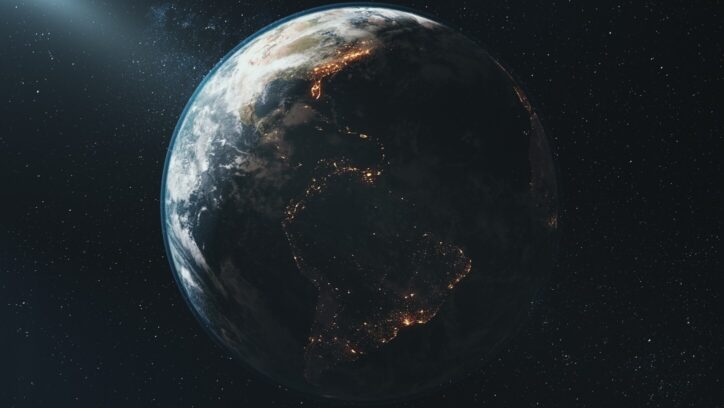

The Earth's axis is tilted, which is the reason we experience seasons. During the course of Earth's orbit around the sun, sometimes it is the North Pole tilting toward the sun and sometimes it is the South Pole tilting toward the sun. In the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in June because the sun's rays hit that part more directly. It is winter in December because then it is the South Pole's turn to be tilted toward the sun. NASA has a diagram showing how the Earth's tilt makes all the difference.
Action on the Sun
Although the Sun's energy output does not change much over time, the Sun is a dynamic star, and its activity level is always changing. Sunspots are darker, cooler areas that appear on the surface of the sun. They are areas of strong magnetic activity. These sunspots can be huge - bigger than the Earth! Sunspots increase and decrease in 11-year cycles. Sometimes there are very few sunspots and the sun seems to be calm and quiet, but at the height of the 11-year sunspot cycle, the number of sunspots increase, and there are many explosive, violent "solar storms."
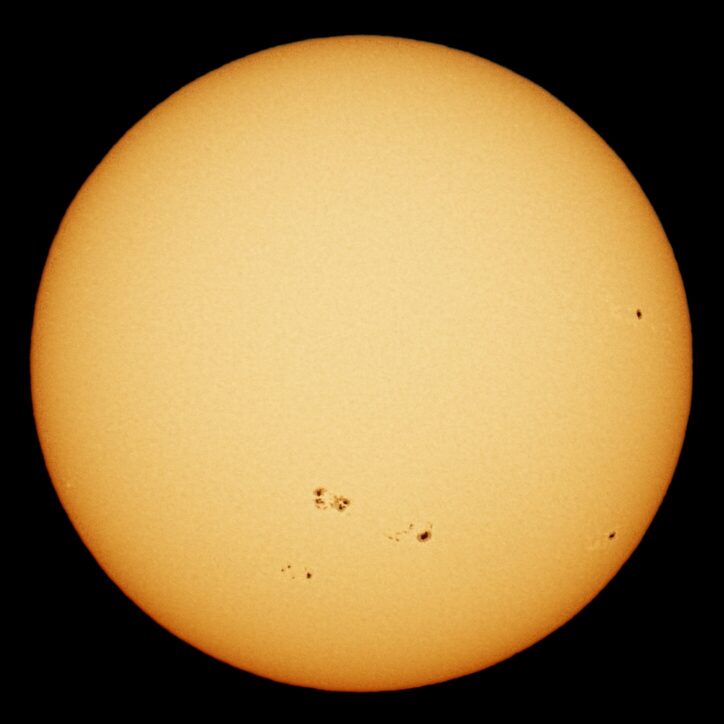

Solar flares happen during times of high solar activity. These are huge explosions on the Sun when massive amounts of gas and plasma are released into its atmosphere. The energy emitted by a solar flare is more than a million times greater than that of a volcanic eruption on Earth. Coronal Mass Ejections are even more powerful, where plumes of gases and solar particles are ejected into space from the Sun's corona, with incredible speed and energy. You can watch an amazing video of a Coronal Mass Ejection as captured by NASA spacecraft.
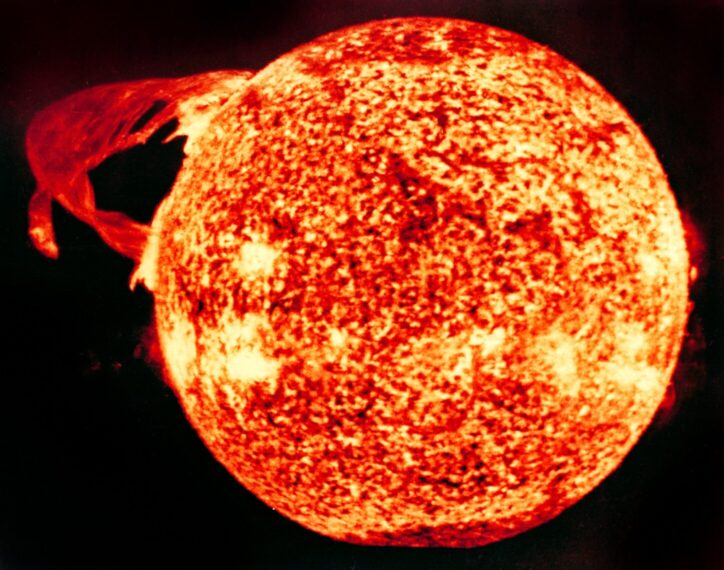
These "solar weather" events are so powerful that they can impact Earth, sometimes damaging radio communications, power grids, and satellites. Such explosions also throw a lot of material out into the solar wind, a stream of radiation and electrically charged particles that flow into space from the surface of the sun.
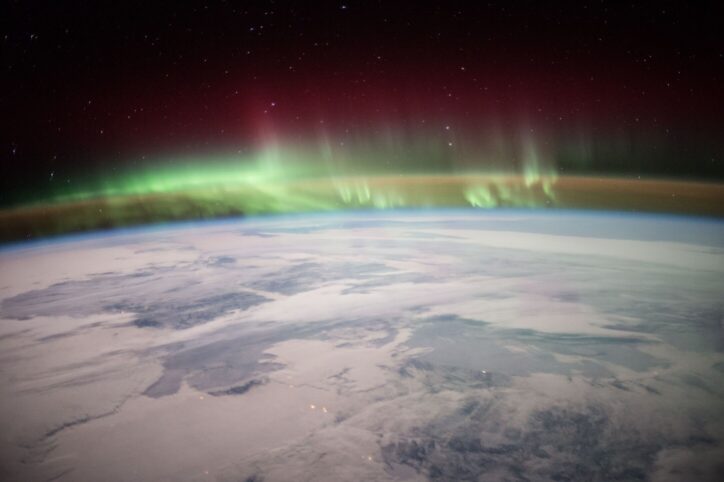
Fortunately, the Earth's magnetic field protects us from the solar wind. But during peak periods of solar activity, particles in the solar wind may interact with gases in Earth's magnetic field. This collision produces auroras, often referred to as the Northern and Southern Lights. Beautiful "light shows" of green, purple, and blue can be seen in the skies near the north and south polar regions. In the northern hemisphere, these lights are called the Aurora Borealis. See a NASA video of how this works. You can learn more about solar weather and solar activity at NASA Space Place. Check it out!

Solar Eclipse
You probably heard about the solar eclipse in August 2017. Did you see it? People travel long distances to see eclipses of the Sun because a total eclipse can only be seen from a small part of the Earth. Eclipses of the sun happen about twice a year, but at any given place on Earth, a total eclipse can be seen only about once every 360 years. So seeing a total eclipse of the sun is a special thing to remember.
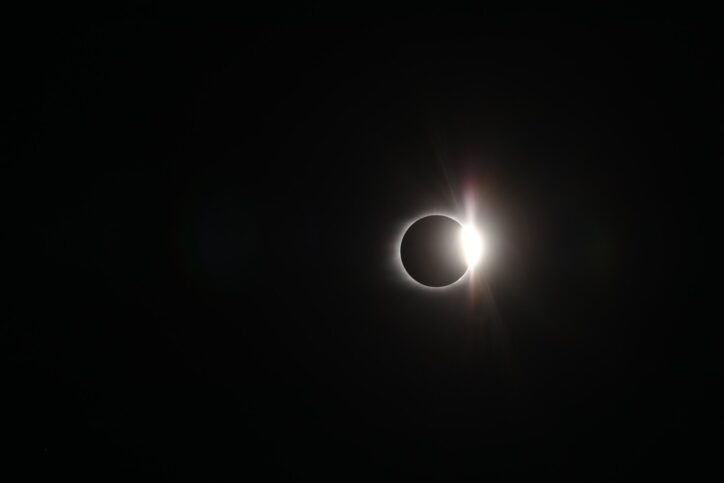

An eclipse of the sun happens when the moon comes directly between the Earth and the Sun. Sometimes there is a partial eclipse, where the moon covers only part of the Sun. In a total eclipse, the moon covers the Sun completely for a short time. People can see a black circle with a ring of light around it — the corona of the sun. The sky goes dark and stars can be seen, even though it may be the middle of the day. Sometimes birds and animals think it is time to sleep. The eclipse lasts no longer than 7 minutes.
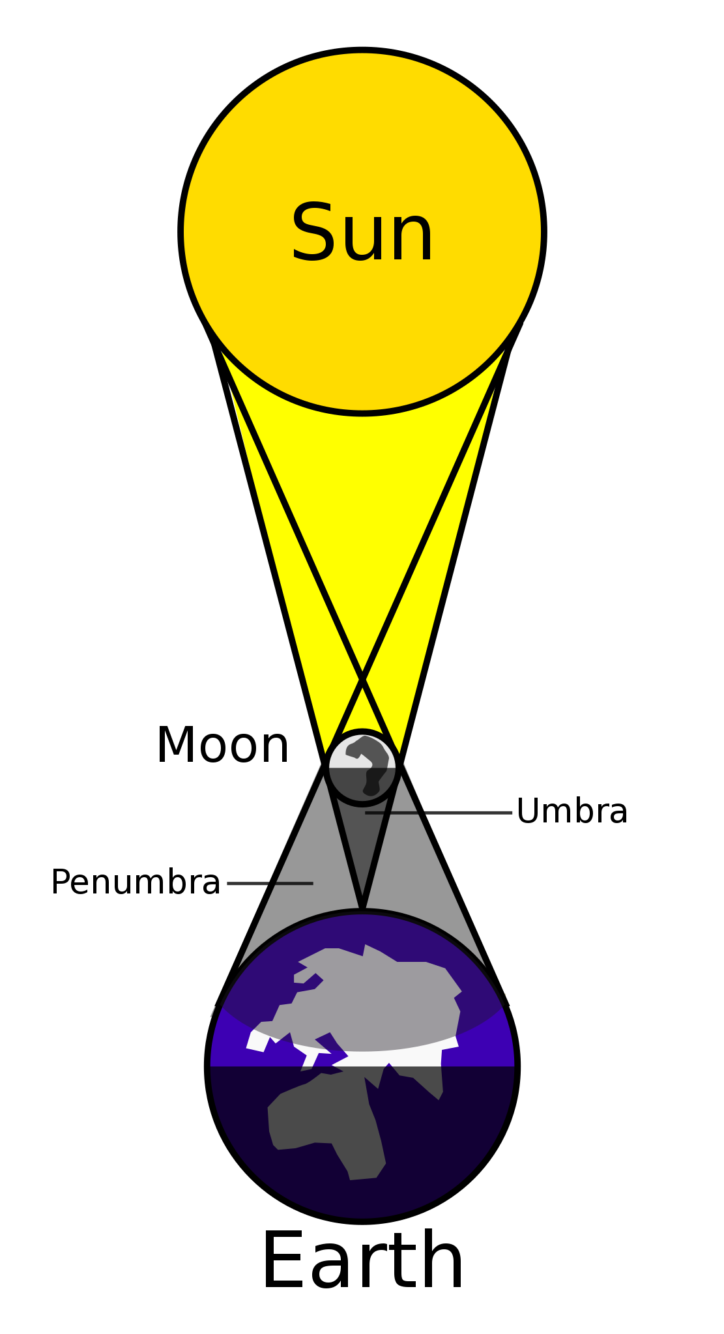
Why can the sun be covered by the moon, since the sun is so much bigger? You know that objects that are closer to you (a soccer ball) can appear larger than objects that are far away (a distant mountain). The Moon may be 400 times smaller than the Sun, but the Sun is 400 times farther away. This means that the moon and the sun appear to be roughly the same size in the sky. So when they line up exactly, the moon is able to cover the gigantic Sun.
It is important never to look directly at the Sun without eye protection. Astronomers use telescopes with special filters to study the sun. During an eclipse, special eclipse glasses can be used.
Studying the Sun

Since humans cannot actually visit the Sun, how do we know what it is like? There are many exciting ways scientists study and learn about the Sun. They can learn about our Sun's age by studying meteorites, the oldest objects from our solar system, and about our Sun's beginnings by studying other stars in various stages of formation with the help of tools such as the Hubble Space Telescope.
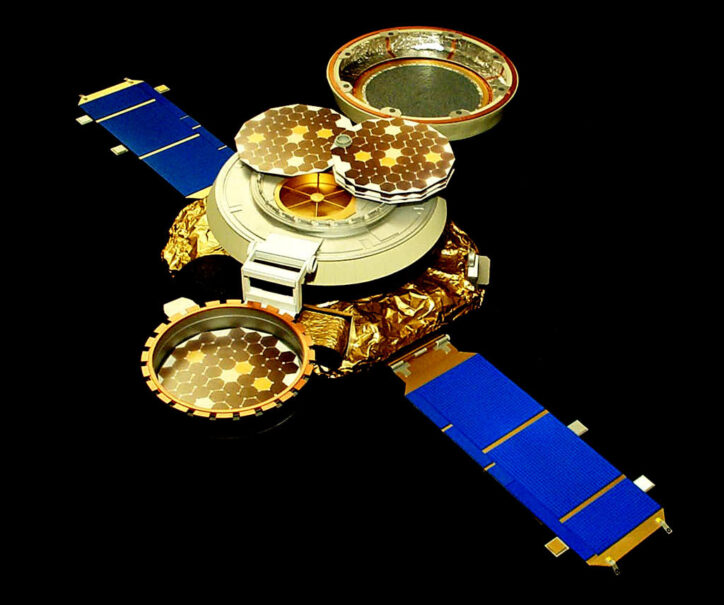

In the last 20 years, there have been several NASA missions to learn more about the Sun and solar processes. The Genesis spacecraft collected particles carried by the solar wind. The Ulysses spacecraft monitored the solar wind intensity and the Sun's magnetic field. STEREO launched in 2006 to study solar storms as they blast from the sun and move out through space. The Geotail mission monitored solar activity to better understand how the sun impacts technology and space exploration. SOHO, the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, is a spacecraft that has been keeping a watch on the sun since 1996. Every day SOHO sends fantastic images back to Earth that help scientists learn about the surface of the Sun and the currents of gas flowing beneath it. It can also warn the Earth of approaching "space weather" events that could disrupt communications or damage satellites.
NASA currently is planning a very exciting project! In 2018, it will launch the Parker Solar Probe to explore the corona of the Sun. The satellite will operate closer to the sun and move faster than anything mankind has ever made!
Fun Facts

Just like the Earth orbits the Sun, the Sun also spins on its axis as it revolves around the Milky Way galaxy. Even though the Sun travels at 136 miles per second, it takes 250 million years for the Sun to complete its orbit through the Milky Way!
The Sun has circled the Milky Way only 20 times since it was formed 4.6 billion years ago.
The Earth gets 94 billion megawatts of energy from the Sun. This is about 40,000 times the power needed by the United States. It is the same as the glow of 4 trillion 100-watt light bulbs!
The Sun creates a massive amount of energy. All the coal, oil, gas, and wood on Earth would only keep the Sun burning for a few days.

A piece one-inch square piece of the Sun's surface would light up 1,500,000 candles!
The total amount of fossil fuels ever used by humans on Earth is less than 30 days of energy reaching the Earth from the Sun.
The Greek word for "sun" is helio, the Roman word for "sun" is sol, and the Greek word for "star" is astro. So you can tell where words like "solar," "astronaut" and "heliosphere" came from!
The years 1645-1715 marked a period of unusually low solar activity when sunspots were rare and the normal 11-year sun cycle closed down. Because this affected Earth's climate, and because the colder climate produced slow-growing trees, scientists theorize that this denser wood caused the famous Stradivarius violins made during that time to have their superior tonal quality. Isn't it amazing how the Sun can affect something like the quality of violins on Earth?
Fun Links
NASA is the place to go to learn, play, create, and enjoy learning more about the Sun. Find out all about current solar storms, eclipses, and probes, including the first mission to touch the sun!
There are many other NASA websites you will want to check out:
NASA's Space Place for Kids has games, crafts, activities, and videos all about the Sun. Check out its terrific gallery of photos of the Sun!
NASA's Star Child is another fun site that includes songs, videos, and activities about the Sun at two different levels.
NASA for Students is a great website you will want to explore. Join NASA Kids' Club, play games, and learn about the solar system, space exploration, astronauts, and all things spacey! There are separate sections for grades K-4 and grades 5-8.
NASA's Solar System for Kids site allows you to click on any object in the solar system. Click on the Sun and find cool facts, a timeline of solar exploration, and amazing images of the Sun sent back to Earth from spacecraft.
NASA's Sun For Kids page has features on mankind's history with the Sun, the amazing work that SOHO is doing, and a 6-minute video about kids like you who study the Sun.
Stanford Solar Center has a great website with activities, videos, games, quizzes, and a fun series of comics, "Tales from Stanford Solar".
Take a look at the European Space Agency's ESA Kids site. You can learn more about eclipses and auroras, do experiments and building projects, and explore space with Paxi, the alien space traveler, through a series of animated videos.
Windows to the Universe is a wonderful place to learn everything you ever wanted to know about the Sun! Take some time to explore this site!
Would you like to interview the Sun? The American Museum of Natural History did! You could act out this "cosmic conversation" with a friend, or put on a play for your classmates.
Take a solar tour to learn more about the Sun from the inside out, and watch solar movies made of images collected from the Yohkoh satellite.
National Geographic Kids has a terrific collection of fun solar system videos, including "Here Comes the Sun" and "Rotation and Revolution."
